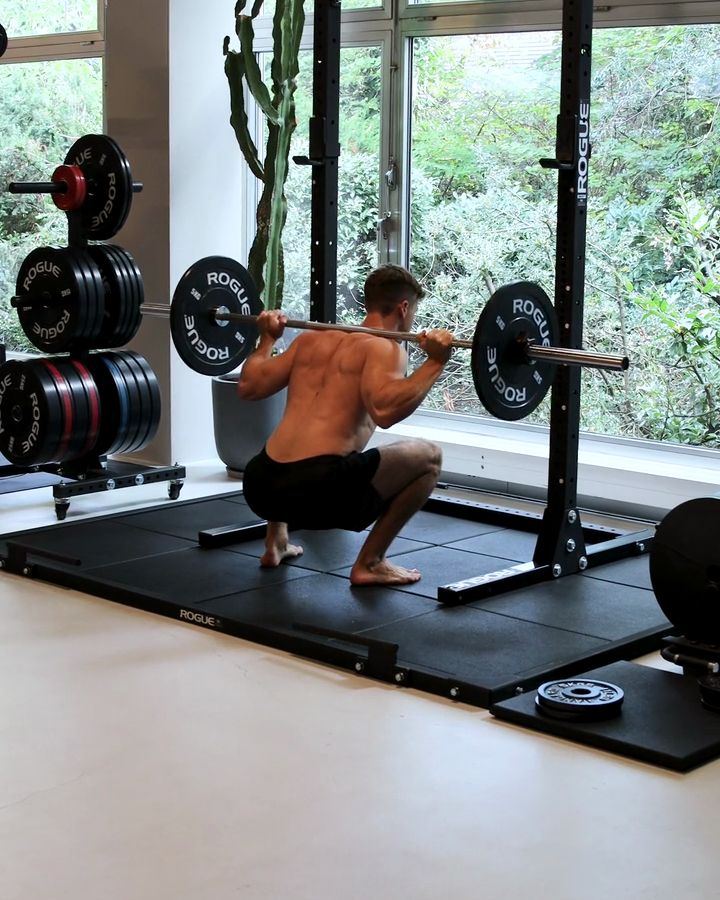
Barbell Back Squats
Back squats are one of the fundamental exercises in strength training. They are typically performed with a barbell, allowing for progressive overload. Back squats primarily target the thigh muscles, particularly the quadriceps and glutes. Additionally, they strengthen the core and lower back, as these muscles are crucial for stability and control during the exercise.
Back squats are among the most well-known foundational exercises in strength training, as they promote overall body strength and stability, improve functional movements in daily life, and, when combined with other strength exercises like deadlifts or lunges, provide an excellent foundation for leg training.
Necessary equipment
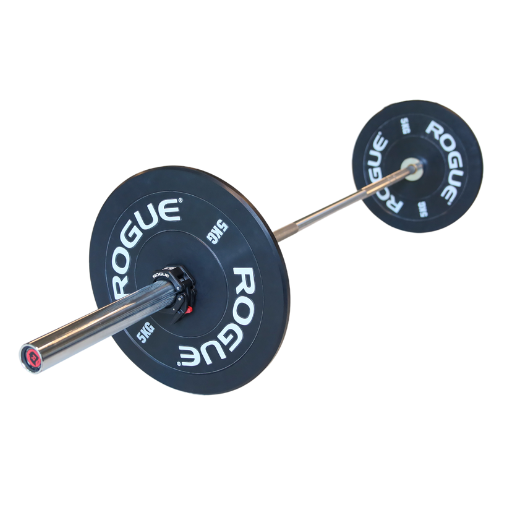

Barbell Back Squats - the correct execution
- Choose a grip width that is comfortable for you, at least shoulder width.
- Stabilize your shoulders by trying to bend the barbell upwards
- Place the barbell on the delta muscle (neck muscles)
- Lift the barbell from the bar with a stable torso and take a small step backwards
- Stand hip to shoulder width apart
- Screw your feet into the floor so that your knees rotate outward
- Toes point forward and are turned slightly outward
- Elbows point down and shoulder blades are pulled back ( retraction)
- Remain as upright in the torso as possible during the squat
- Bend the knees and lower your hips below the knees
- The thigh should be at least parallel to the floor
- Then stretch your legs with tense buttocks
- Keep tension in torso, shoulder girdle and buttocks throughout
- The training weight for this exercise is the sum of the barbell's own weight and the additional weight plates
The exercise Back Squats is intended to be used as a hypertrophy exercise.
Which muscles are trained by Back Squats?










Primary trained muscles for Back Squats
Quadriceps - The quadriceps femoris is the large muscle at the front of your thigh. It extends your knee.
Secondary trained muscles for Back Squats
Lower Back - The erector spinae muscle runs along your spine and helps you extend your back and stand upright.
Adductors - The adductors are muscle groups in the thigh that help bring your legs together. They stabilize your pelvis while walking and standing and also assist in movements like crossing your legs.
Glutes - The gluteus maximus is the large muscle in your buttocks. It is important for extending the hip, moving your leg backward, and stabilizing the hip joint.
Similar exercises to Back Squats
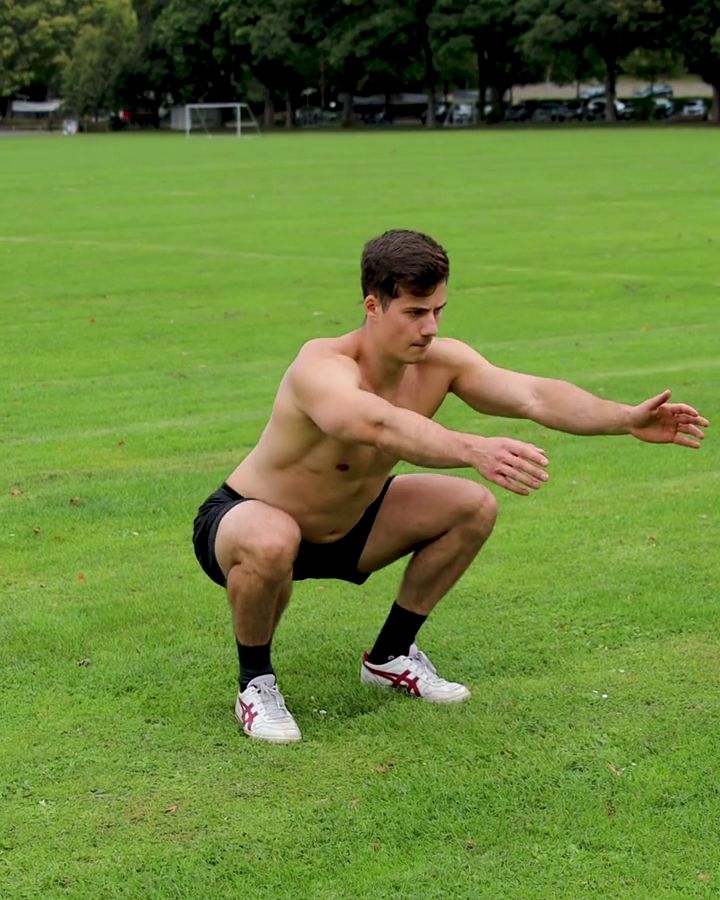
Bodyweight Squats
The bodyweight squat is probably the most well-known fitness exercise in the world. It strengthens your legs and glutes. However, it is not as easy to perform as it looks. Many still think that it's bad to push the knees beyond the toes. This myth has long been debunked. Much more important is that you perform the movement slowly and controlled, gradually increasing it. If you can perform 20-30 bodyweight squats, then goblet squats, barbell squats, or assisted single-leg squats could be a great progression.
Curtsey Lunges
Curtsey lunges are a variation of the classic lunge, where the back leg is crossed behind the body. This movement particularly targets the outer thighs and glutes, especially the side glute muscles. The crossing motion also promotes knee joint stability and improves coordination. Compared to the normal lunge, curtsey lunges work the side muscle groups more intensively, making them an effective exercise for balanced leg training.
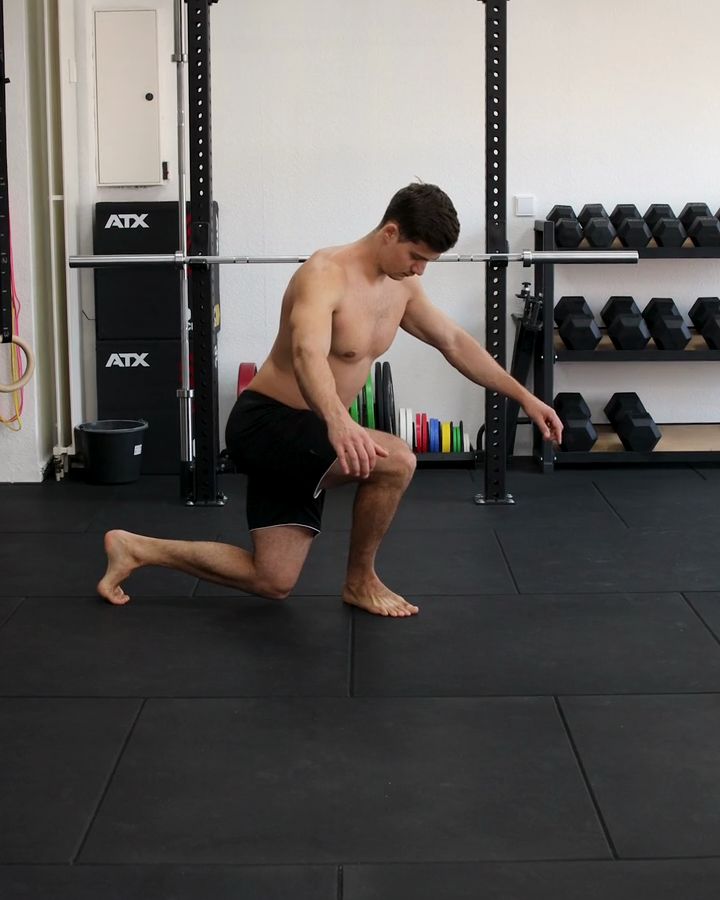
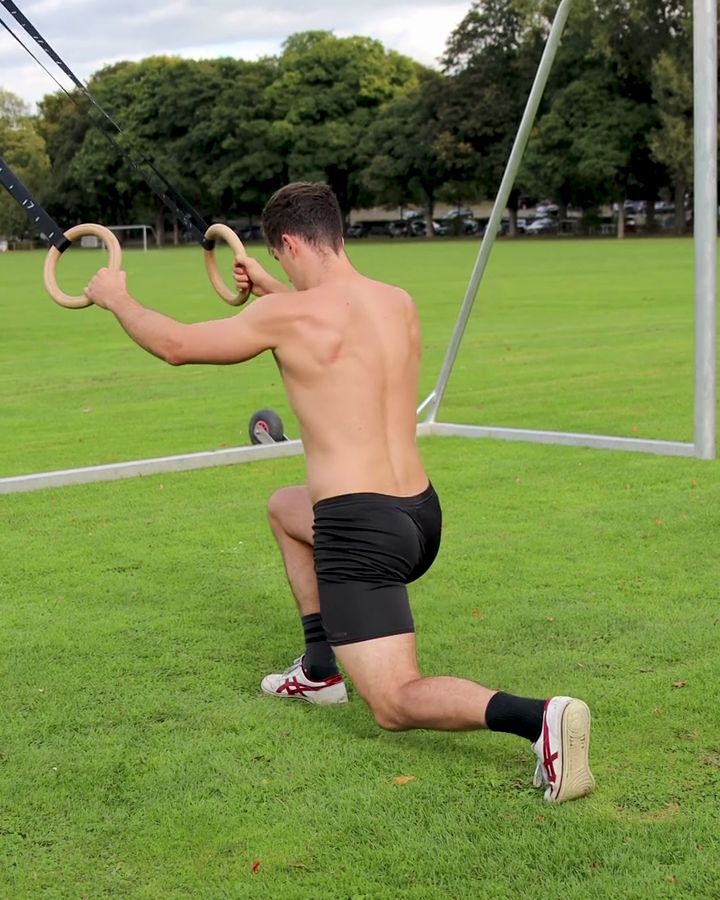
Assisted Lunges
Supported lunges with gymnastic rings are an excellent exercise, especially for beginners. They specifically target the leg muscles, particularly the quadriceps and glutes, while the rings provide additional stability and balance. This support reduces the risk of injury and makes it easier to perform the exercise correctly. At the same time, the movement promotes hip mobility and increases leg strength, forming the foundation for more advanced exercises.
A variation of this exercise is performing regular lunges without support or with added weight. Unlike supported lunges, these require more balance and greater control of movement.
This could also be interesting

Calisthenics Body Transformation – How to Build a Strong, Lean, and Athletic Physique
Transform your body with Calisthenics! Build muscle, burn fat & achieve a shredded physique with bodyweight training. See real before & after results!
The Best Fitness Apps in 2025: Our Top 10 Recommendations
Don’t miss the best fitness apps of 2025: surprising favorites, free options, and perfect tools for your workouts. Find the ideal app today!

Complete Calisthenics Skills List – 40+ Exercises from Beginner to Pro
Which calisthenics skills should you learn first? And which ones will really help you progress? In this article, you’ll find a complete list of over 40 exercises – from the very basics to the toughest moves for professionals. Each exercise comes with instructions, so you can immediately integrate them into your training.