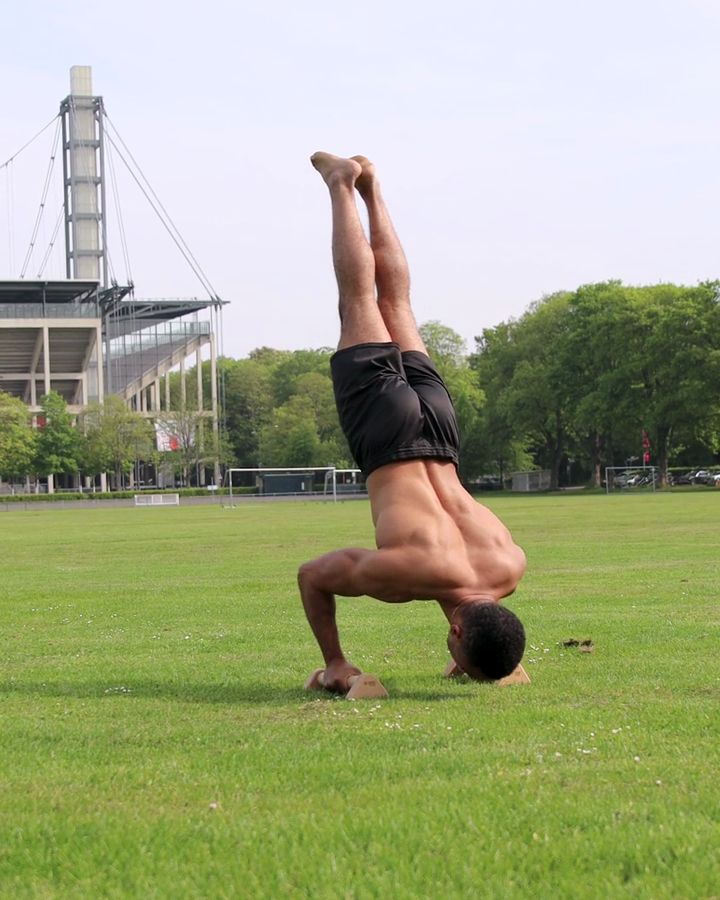
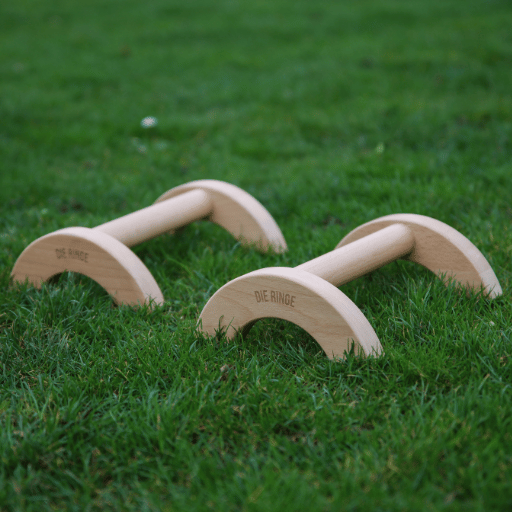
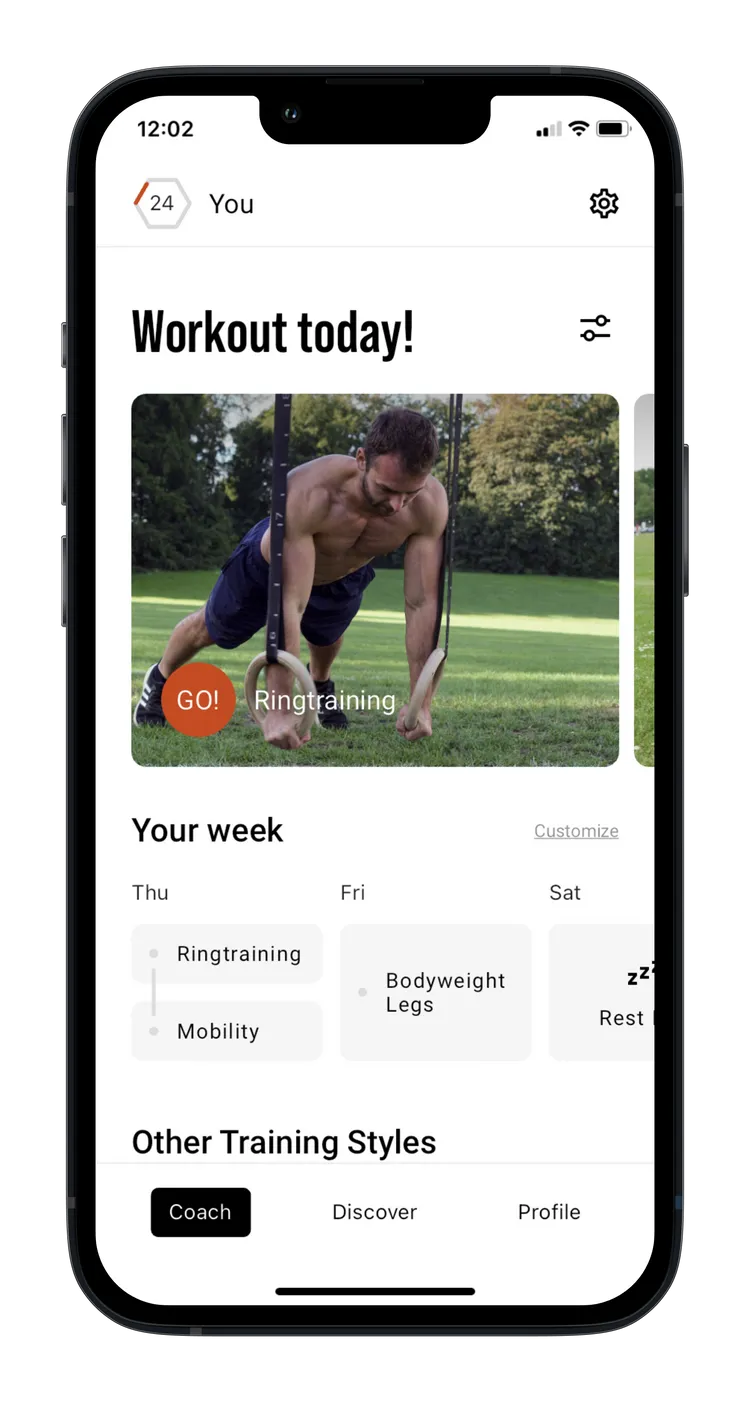
Handstand Push Ups with parallettes
Handstand push-ups on parallettes require a great deal of stability, strength, and coordination, as they are performed in a handstand position. Compared to regular push-ups, this exercise is much more intense, as you need to lift your entire body weight. It requires a stable handstand position and significant shoulder strength, making it a common advanced progression from exercises like Pike Push-Ups or wall handstand push-ups.
Necessary equipment
Handstand Push Ups with parallettes - the correct execution
- Start in handstand
- Bend your elbows
- Bring your head towards the floor
- Nose pointing towards the floor
- Keep maximum tension in core and glutes
- Press back into handstand
The exercise Handstand Push Ups is intended to be used as a technique, hypertrophy exercise.
Which muscles are trained by Handstand Push Ups?
















Primary trained muscles for Handstand Push Ups
Upper Back - The muscles in the upper back, including the trapezius and rhomboid muscles, help move and stabilize your shoulders. They pull the shoulder blades together and support posture.
Front Delts - The front part of the deltoid muscle, also known as the anterior shoulder, is located at the front of the shoulder. It is primarily involved in the forward movement of the arm, such as lifting the arm forward. It also assists in the internal rotation of the arm. This muscle is engaged in activities that involve lifting objects in front of the body or pushing forward.
Secondary trained muscles for Handstand Push Ups
Triceps - The triceps brachii muscle is located at the back of your upper arm. It extends your arm at the elbow and also helps move the arm backward.
Neck - The neck muscles move your head in all directions and support important structures such as blood vessels and nerves that run between your head and chest.
Abs - The rectus abdominis, also known as the "abs," runs vertically along the front of the abdomen. It is responsible for bending the torso forward, such as during sit-ups, and lifting the pelvis. This muscle stabilizes the torso, supports the spine, and helps maintain good posture.
Forearm - The forearm muscles are divided into flexors and extensors. The flexors bend your wrist, while the extensors straighten it.
Side Delts - The lateral part of the deltoid muscle, also known as the lateral shoulder, is located on the outside of the shoulder. It is the main muscle responsible for lifting the arm sideways. The lateral shoulder is particularly active when the arm is extended away from the body, such as during lateral raises or lifting objects to the side. It plays a key role in arm abduction and shoulder stabilization.
This could also be interesting

Calisthenics Body Transformation – How to Build a Strong, Lean, and Athletic Physique
Transform your body with Calisthenics! Build muscle, burn fat & achieve a shredded physique with bodyweight training. See real before & after results!
The Best Fitness Apps in 2025: Our Top 10 Recommendations
Don’t miss the best fitness apps of 2025: surprising favorites, free options, and perfect tools for your workouts. Find the ideal app today!

Complete Calisthenics Skills List – 40+ Exercises from Beginner to Pro
Which calisthenics skills should you learn first? And which ones will really help you progress? In this article, you’ll find a complete list of over 40 exercises – from the very basics to the toughest moves for professionals. Each exercise comes with instructions, so you can immediately integrate them into your training.